Innovations In the Management of Diabetes

Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disease that leads to high blood glucose or blood sugar. Diabetes is a growing challenge in India with an estimated 77 million people living with diabetes which makes it the second most affected in the world. Fortunately, substantial progress has been made in diabetes management with promising results using different treatment regimen. Here's a look at some of the most promising innovations in the diabetes management
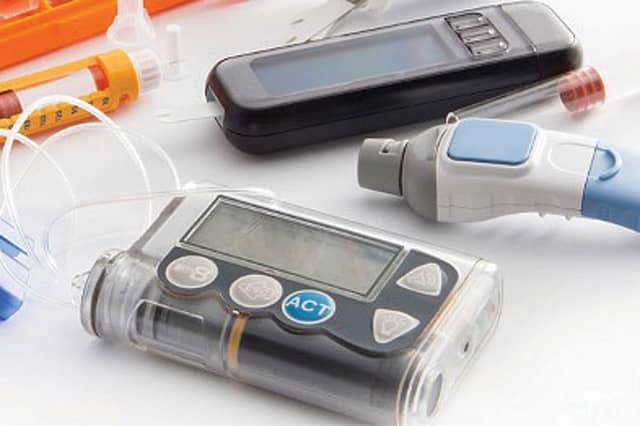
1. Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): CGMs, are small devices, often about the size of a quarter that use a small under-the-skin needle to continuously monitor blood-glucose levels. This information can be transmitted in some cases wirelessly and automatically to a smartphone app or other device. You can look at glucose levels for a single point in time, but you can also look at trends in values over time. For example, monitoring blood sugar in real time could help people make diet or lifestyle changes. CGMs also help improving "Time in range" blood glucose values in type 1 diabetes.
DIABETES2. Insulin Delivery Systems: Advances in insulin delivery technology, such as insulin pumps and smart pens, have improved insulin administration and made it more convenient. Smart insulin pens can provide precise dosing and even offer reminders for insulin injections. Advancement in the insulin pump include, Automated insulin delivery systems (artificial pancreas). Hybrid Closed Loop systems can modulate delivery both up and down, although users still initiate insulin doses (boluses) for meals. Fully Closed Loops require no manual insulin delivery actions or announcement for meals.
3. Newer drugs: Two types of drugs are emerging as potential "game changers" when it comes to Type 2 diabetes treatment. Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) is a hormone released in the gut during digestion—one that plays a role in blood-sugar homeostasis. GLP-1 receptor agonists can interact with GLP-1 receptors in ways that lower appetite, improve glycemic control, and promote weight loss for people with Type 2 diabetes. Semaglutide is one such drug which is also available in the pill form. Recently approved tirzepatide is the first-in-class medication that activates the receptors for both glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and has a remarkable impact on weight loss and glycemic control. A second category of drug has also emerged as a standout in the treatment of Type 2 diabetes. Known as sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors, these drugs help the kidneys remove sugar from a person's blood. Not only does this improve blood-sugar control in people with Type 2 diabetes, but it also helps protect them from heart failure and kidney disease.
4. Bariatric surgery: For some individuals with type 2 diabetes and severe obesity, bariatric surgery has been a transformative treatment option. It can lead to significant weight loss and often results in remission of diabetes. In the future, these procedures are likely to become more commonplace even for people with Type 2 diabetes who are not severely obese.
5. Telemedicine: The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of telemedicine. People with type 2 diabetes can now consult with healthcare providers remotely, making it easier to manage their condition while reducing the need for in-person visits.
6. Gene therapy and stem cell therapy: These therapies hold a lot of promise for people living with T1D who are hoping for an eventual future without needing to take insulin or immuno suppressant therapy. Some gene therapy and stem cell approaches in type 2 diabetes research have explored potential metabolic gene targets that might help improve insulin sensitivity or glucose regulation. Gene and stem cell therapy for the treatment of diabetes is an area of ongoing research and development. These therapies as a routine treatment for diabetes have not yet reached the stage of widespread clinical use.
7. Dietary interventions: There have been research on a number of weight-loss diets. Some of the latest studies suggest that fasting plans in particular, intermittent fasting may be particularly beneficial for people with Type 2 diabetes. Intermittent fasting involves cutting out calorie-containing foods and drinks for an extended period of time anywhere from 12 hours to two days depending on the approach a person chooses.
Combining lifestyle changes along with innovative therapies can help people manage their diabetes well and improve quality of life.
(A marketing initiative by Open Avenues)